Vitamin D Benefits, Types, Sources, Supplements & Dose
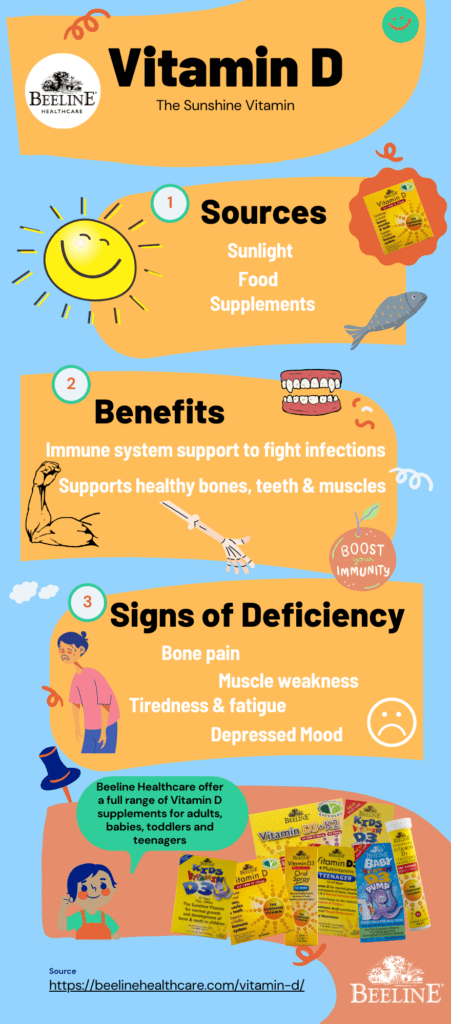
Vitamin D is the sunshine vitamin. The benefits of vitamin D include healthy bones, teeth, muscles, and a properly functioning immune system. Sources include sunlight, food, and vitamin D supplements. Signs of Vitamin D deficiency include bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, and a depressed mood.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for good health and has been associated with many health benefits. It helps the body function properly to stay healthy.
Types of Vitamin D
There are two major types of vitamin D. These are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
The human body does not produce vitamin D2. It comes from plants such as mushrooms.
We can produce vitamin D3 in the skin when exposed to sufficient sunlight.
Conventional Vitamin D3 is obtained from animal origins including lanolin (sheep wool grease) or animal skins. It is also now available from plant sources, so it is suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
What are the Benefits of Vitamin D?
Why we need vitamin D is that is vital for good health. A key benefit of vitamin D includes is that it supports a properly functioning immune system to fight infections. Other benefits of vitamin D include the nutrients within it playing a key role in developing and maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles.
Research has linked vitamin D to reducing the risk of some cancers.
It helps fight infection, which is recommended as a tool in combating coronavirus. Recent studies provide evidence that vitamin D can help reduce the severity of Covid-19, provided there are adequate levels of vitamin D in the body.
Furthermore, some studies also suggest it helps support a healthy heart, lungs, and brain.
How Much Vitamin D Should You Take?
Taking a daily vitamin D supplement for adults between 20 µg (800 IU) and 25 µg (1000 IU) daily is recommended, and potentially higher dosage for vulnerable people under medical supervision. Children should take 10µg (400 IU) daily.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is not having enough vitamin D in your body. Symptoms of deficiency can include bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, and a depressed mood.
Among the more severe results of vitamin D deficiency are rickets in children as well as osteomalacia in adults. Both are characterised by loss of minerals from the bones and result in skeletal deformities such as bowed legs, retarded growth, and inadequate mineralisation of tooth enamel and dentin. The link between vitamin D deficiency and the onset of osteoporosis in the elderly has been widely studied.
Who is at Risk of Vitamin D Deficiency?
You may be at risk of having a deficiency if you:
- Do not get enough sunshine by avoiding the sun or covering up from sunlight.
- Have darker skin.
- Are older or have a condition, so you do not get outdoors enough.
- Are a pregnant woman.
- Are a baby.
- Have a vitamin D metabolism health condition.
- Are vegetarian or vegan.
How Do We Get Vitamin D?
We get it from these sources:
- Exposure to sunlight.
- Food.
- Supplements.
Sunshine
Vitamin D is called the sunshine vitamin. This is because we get it from the sun. When the sunlight’s ultraviolet (UV) rays touch our skin, our bodies convert this into vitamin D3. The amount of vitamin D we produce is impacted by the year’s season, an individual’s skin colour, age, and how much of our skin is exposed to sunlight. Higher levels of vitamin D are generally available from sunlight outdoors during Summer and Spring in Ireland. Due to the risk of skin cancer from harmful UV rays, people mustn’t overexpose to the sun or get sunburnt.
During the Autumn and Winter months, people in Ireland generally do not get enough sunlight. Therefore, a vitamin D supplement can help.
Food
Vitamin D can also be accessed via certain food that is rich in this vitamin and from eating a balanced healthy diet. Food that can be good sources include:
- Oily fish such as mackerel, tuna, salmon, herring, and sardines
- Red meat.
- Liver.
- Fortified foods such as breakfast cereals.
- Dairy products such as cheese and egg yolks.
- Orange juice.
- Soy milk.
- Cod liver oil.
Vitamin D Supplements
Dietary supplements are another source. Beeline Healthcare offers a full range of vitamin D supplements for adults, babies, toddlers, and teenagers. This helps combat vitamin D deficiency.
The Health Service Executive (HSE) recommends vitamin D supplements for all babies 0 to 12 months old. The Food Safety Authority of Ireland (FSAI) recommends during the extended Winter months from Halloween to St Patrick’s Day, that all children aged 1 to 5 years old need to be given a low-dose (5 μg) vitamin D-only supplement. This will help make up for the lack of skin synthesis of vitamin D from sunlight during this season. The NHS recommends a daily supplement for children aged 1 to 4 years old of 10 micrograms of vitamin D.
Vitamin D plays a key role in a healthy life fighting infection and disease, while reducing depression. It is vital for healthy and immune system, bones, teeth and muscles.
Sunlight along with a balanced healthy diet and supplements combine to combat vitamin D deficiency for all ages.
Beeline Vitamin D Supplements
Vitamin D Infographic
Share this Image On Your Site
Questions Vitamin D
- What are the benefits of vitamin D?
The benefits of vitamin D include healthy bones, teeth, muscles and a properly functioning immune system.
- What are the best sources of vitamin D?The best sources of vitamin D are:
- Exposure of our skin to sunlight’s ultraviolet rays produce vitamin D.
- Food including oily fish red meat.
- Vitamin D supplements.
- How much vitamin D should you take?It is recommended that adults take a daily vitamin D supplement of between 20 µg (800 IU) and 25 µg (1000 IU) every day. For vulnerable people, a potentially higher dosage than normal may be recommended under medical supervision. Children are should take 10µg (400 IU) daily.
- What foods are high in vitamin D?Foods that are high in the vitamin D include fatty oily fish such as mackerel, tuna, salmon, herring and sardines, red meat, liver, fortified foods such as breakfast cereals, dairy products such as cheese and egg yolks, orange juice, soy milk and cod liver oil.
- What are the types of vitamin D?There are two major types of vitamin D. These are vitamin D2 ergocalciferol, and vitamin D3 cholecalciferol. Vitamin D2 is not produced by the human body. Sources include plants such as mushrooms. Vitamin D3 is produced naturally in the skin, when exposed to sufficient sunlight. Other source include supplements and certain foods such as oily fish.


