Folic Acid Benefits and Sources
Folic acid is the man-made synthetic form of folate, also called vitamin B9. It reduces the risk of common birth defects as well as having benefits for red blood cells, depression and heart disease. Folic Acid sources include certain foods and dietary supplements.
What is Folate?
Folate is another name for vitamin B9. It is an essential vitamin that is needed for good health for everybody, and for good prenatal health for mother’s unborn babies.
Folate is important to help our bodies produce DNA, new cells, other genetic material and healthy red blood cells. Our bodies cannot produce folate naturally or store it for any length of time, so it must be ingested regularly through our diet.
What is Folic Acid?
Folic acid is the man-made synthetic form of folate. Found in certain foods and dietary folic acid supplements, folic acid is converted into folate by the body.
What are Neural Tube Defects?
Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain, spine or spinal cord in babies. Spina bifida is a type of neural tube defect that occurs when a baby’s spine and spinal cord does not form properly in the womb. The impact of spina bifida is that it can cause disabilities in babies, which can range from mild to severe.
The possibility of neural tube defects in babies increase when a mother does not have enough folate in their body both before and during pregnancy. Therefore, folic acid supplementation is recommended.
What are the Benefits of Folic Acid and Folate?
What is folic acid good for? The benefits of folate and folic acid include:
- Reducing the risk of congenital deformities and common birth defects such as spina bifida. Folic acid helps prevent pregnant women giving birth to babies with neural tube defects by preventing neural tube defects in the central nervous system. Folic acid contributes to the normal development of unborn babies’ nervous systems, brains, skulls and spinal cords.
- Helping the body produce healthy red blood cells, which assist preventing folate deficiency anaemia. Red blood cells carry oxygen around our bodies, which contributes to physical function, cognitive function and the development of the body. Folate deficiency anaemia can occur when a lack of folate causes the body to produce larger than normal red blood cells that do not function properly.
- Lowering the risk of heart disease by contributing to maintenance a healthy heart. Homocysteine is a blood protein. High levels of homocysteine in the blood is considered a risk factor for most forms of heart disease. Folic acid can help reduce the levels of homocysteine, which supports a healthy heart and reduces the risk of heart disease. A study published in May 1966 in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that people who suffered heart attacks had lower levels of both dietary and plasma folic acid.
- Potentially reducing the risk of stroke for those with cardiovascular disease by lowering homocysteine levels.
- Helping the body produce, maintain and repair healthy functioning cells. These cells include those found in the organs, bones, skin, hair and nails.
- Potentially reducing the risk of cancers by helping prevent changes to DNA and cells that may lead to certain types of cancers such as lung, pancreatic, throat, stomach, cervical, ovarian and breast cancers.
- Reducing risk of depression. Studies have shown links between folate deficiency and depression, with suggestions that low folate levels may be detrimental to our mood. A study by Alec Coppen and Christina Bolander-Gouaille has recommended that folic acid should be considered as part of treatment plan for depression.
- Improving brain health. A number of studies shown links between low levels of folate and increased risk of mental impairment issues in older adults.
Sources of Folate and Folic Acid
The sources of folate are certain types of food and dietary supplements.
1. Food
Folate or vitamin B9 can be found naturally in many foods, while folic acid is added to many fortified foods for health benefits.
Foods rich in folate or folic acid include:
• Asparagus.
• Avocado.
• Eggs.
• Broccoli.
• Brussels sprouts.
• Legumes.
• Leafy green vegetables, such as cabbage, kale, spring greens and spinach.
• Peas, chickpeas and kidney beans.
• Nuts and seeds.
• Breakfast cereals and grains fortified with folic acid.
• Citrus fruits.
• Bananas.
• Liver.
2. Folic Acid Supplements
Dietary supplements are the second source of vitamin B9. Beeline Healthcare have a number of folic acid supplements to provide the recommended daily allowance.
Beeline Folic Acid Tablets
Beeline Folic Acid Tablets play a vital role in the prevention of serious birth defects and contribute to normal maternal tissue growth during pregnancy. It can also contribute to preventing heart disease. It is recommended that folic acid tablets be taken for 14 weeks prior to pregnancy and for 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Beeline Vitality Tablets
Beeline Vitality Tablets contain iron, vitamin D and folic acid. They provide triple action nutrition support for women’s general health, vitality and wellbeing.
Who Should Take Folic Acid?
Folic Acid is highly recommended for women of childbearing age. During pregnancy, folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects developing in the foetus. It is recommended that folic acid be taken for at least 14 weeks prior to pregnancy and for 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Consuming sufficient levels of folate is very important during life stages of bodily growth such as during adolescence, infancy or pregnancy. Folic Acid can be used to treat or prevent folate deficiency anaemia. Most adults and children can take folic acid but it is not suitable for everyone. People are advised to consult your doctor beforehand.
Recommended Intake of Folic Acid
According to the HSE, adults need 0.2mg of folate per day. They recommend a daily supplement 0.4mg of folic acid for pregnant women or those thinking of getting pregnant.

Folic Acid Infographic
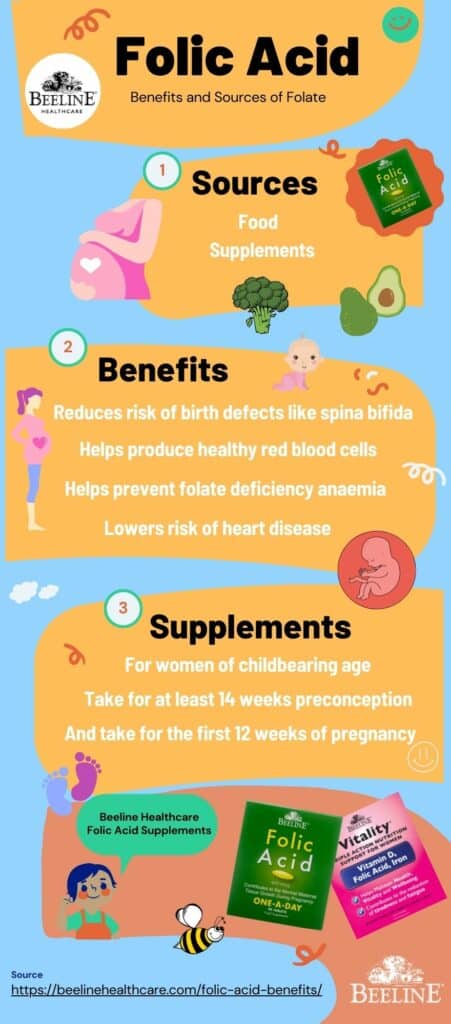
Share this Image On Your Site
Questions Folic Acid
- What are the Benefits of Folic Acid?
The benefits of folic acid are:
- Reducing the risk of congenital deformities and common birth defects such as spina bifida.
- Helping the body produce healthy red blood cells, which carries oxygen around our bodies and helps prevent folate deficiency anaemia.
- Lowering the risk of heart disease by contributing to maintenance a healthy heart.
- Potentially reducing the risk of stroke for those with cardiovascular disease by lowering homocysteine levels.
- Helping the body produce, maintain and repair healthy functioning cells.
- Reducing risk of depression.
- Contributing to brain health.
- Potentially may help reduce the risk of certain cancers by helping prevent changes to DNA and cells that may lead to certain types of cancers.
- What is Folic Acid?Folic acid is the man-made synthetic form of folate, also called vitamin B9. It is sourced in certain types of fortified foods and dietary supplements. Folic acid is converted into folate by our bodies, and is essential for good health and good prenatal health.
- What does folic acid do for the body?Folic acid contributes to good health. It provides folate to help our bodies produce DNA and healthy red blood cells, while assisting prevent folate deficiency anaemia. Folic acid is especially important before and during pregnancy to help prevent neural tube defects such as spina bifida in babies.
- Is it good to take folic acid every day?Yes, it is good to take the recommended dose of folic acid every day. The Health Service Executive in Ireland recommend a dose of 400 micrograms of a folic acid supplement every day.


